Paralysis and motor dysfunction after stroke result from damage to areas of the brain involved in movement. Therefore, recovery of motor function requires rebuilding damaged brain function and having the cerebral nervous system relearn how to move.
Neurorehabilitation is a new method of rehabilitation based on neuroscience, where patients relearn motor functions through restructuring neural pathways in the cerebrum.
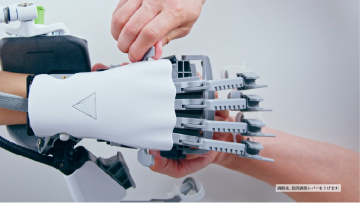
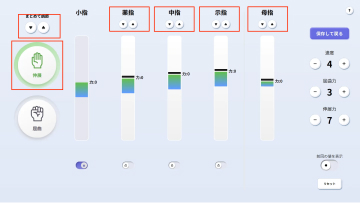
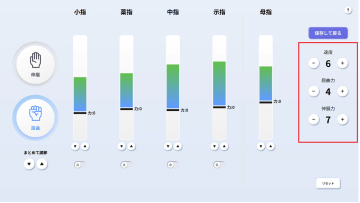
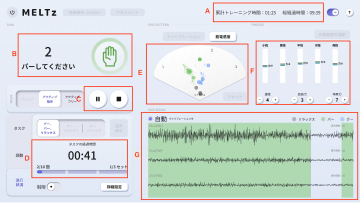
MELTz uses an AI based on proprietary algorithms to comprehensively analyze the electrical signals in the patient's forearm. As a result, it provides more opportunities for rehabilitation by recognizing the hand movement that the patient is trying to perform and accurately reproducing the same movement repeatedly using robotic assistance. Providing movement assistance in conjunction with motor intent encourages the cerebral nervous system to relearn these movements.